The United States Senate approved a bill this month, including $52 billion for funding semiconductor research, design and manufacturing. The bill was supported by the United States House of Representatives and President Biden.
Japan's Ministry of Economy and Industry announced a "national project" earlier this month to support Japan's semiconductor manufacturing.
In May, South Korea announced a plan to spend $450 billion on non-memory semiconductor manufacturing in the next decade, which will be paid by private enterprises and government tax credits.
The European Union announced in May that it was ready to invest "a large amount" of funds to expand the semiconductor manufacturing in Europe.
According to IC Insights, the total capital expenditure (CapEx) of the semiconductor industry in 2020 is 113 billion US dollars. The growth forecast for 2021 is between 16% and 23%.
The forecast for 2021 is mainly made in April after the release of the first quarter's earnings. Many of these figures may be revised upwards during 2021.
During the period of high demand, a large amount of investment was made to expand production capacity. When the growth of demand slowed or decreased, overcapacity would lead to a decline in income.
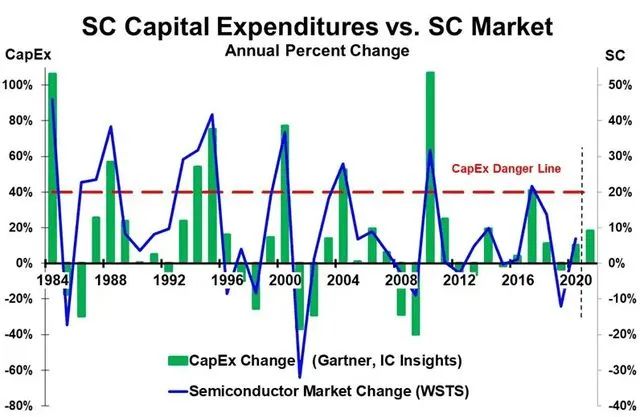
After the sharp increase of semiconductor capital expenditure, the semiconductor market will decline (or significantly decelerate) within one to two years. When the semiconductor market grew by 46% in 1984, the capital expenditure increased by 106%; The semiconductor market fell by 17% in 1985. In 1989, the semiconductor market slowed by 30 percentage points to 8% growth.
In 2000, at the peak of the Internet boom, the semiconductor market grew by 37%; At the same time, capital expenditure increased by 77%. In 2001, the market experienced the largest decline in history, at 32%. The decline of the semiconductor market in 2008 and 2009 was caused by the global financial crisis. In 2010, it recovered a strong growth of 32% and capital expenditure increased by 107%.
There are many factors affecting the growth rate of the semiconductor market, including the overall economy and the demand for key electronic products. However, when demand slows down, a large increase in capacity will always lead to overcapacity. The overcapacity has led to the decline in the price of semiconductors, especially the bulk commodities such as memory. Inventory held by electronic manufacturers and distributors has been reduced. Such overcapacity often occurs after capital expenditure increases by more than 40%. This is indicated by the red capital expenditure hazard line in the figure. It is estimated that the capital expenditure growth in 2021 will be between 16% and 23%, and the industry is far from the "danger line" of more than 40% growth. Even if the growth of capital expenditure accelerates in the second half of 2021, it is unlikely to exceed 30%. TMSC is satisfied with the 74% increase in capital expenditure, because it has many customers of the OEM factory who require to increase production capacity. The other two generation plants, Liandian and GlobalFoundries, both plan to increase their capital expenditure by at least twice in 2021 compared with 2020.
Although the current situation does not predict the recent overcapacity of semiconductors, it is worthy of attention in the next few years. It remains to be seen to what extent the current semiconductor shortage is due to the short-term interruption caused by the pandemic, and to what extent is due to the increase in demand for electronic equipment and the increase in semiconductor content.
 ch
ch English
English

